How vaping works: from e-liquid to vapor cloud?
Vaping may look futuristic, but the science behind it is simple. At its core, an e-cigarette is just a small device that heats up liquid and turns it into an inhalable mist — or more technically, an aerosol. But how does that really happen? And what’s inside that cloud? Let’s break it down step by step.
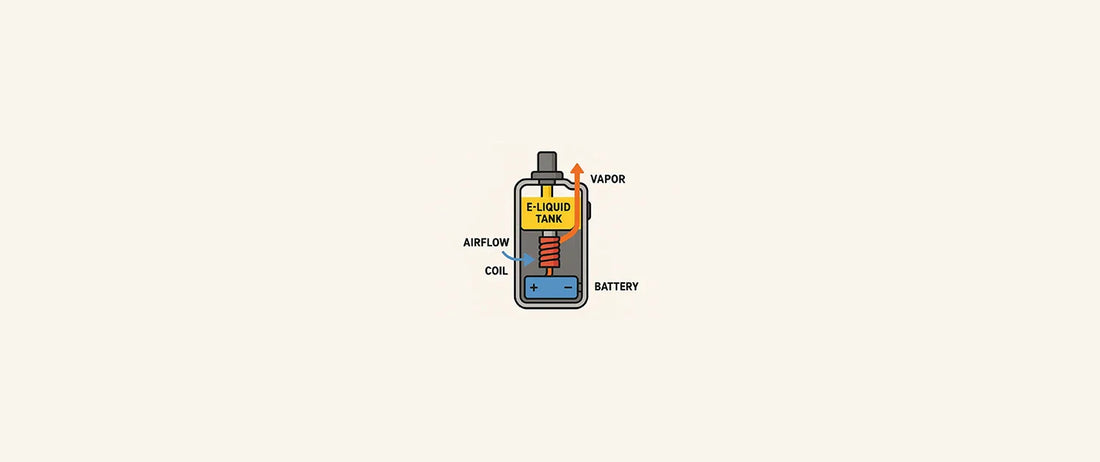
The key components of a vape
All vape devices, whether pods, pens or box mods, follow the same basic structure:
- Battery: powers the device and heats the coil.
- Coil (or heating element): a small metal wire that gets hot when current passes through.
- Wick: usually cotton, it soaks up the e-liquid from the tank or pod.
- E-liquid: a mix of propylene glycol (PG), vegetable glycerine (VG), flavourings, and optional nicotine.
- Tank or pod: holds the e-liquid and delivers it to the coil through the wick.
Once the device is activated — either by pressing a button or simply inhaling — the battery sends power to the coil. The coil heats up, vaporising the liquid held in the wick.
From liquid to vapor: the science
Unlike smoke, which is the result of combustion (burning), vapor is created through a process called aerosolisation. This involves heating the liquid to around 200–250°C, just enough to turn it into a mist without burning anything.
The result? A cloud of tiny droplets that carry flavour and (if included) nicotine — but far fewer harmful substances than cigarette smoke.
What’s actually in the vapor?
- Water and PG/VG base: the main carriers of the vapor.
- Flavourings: food-grade compounds that provide taste.
- Nicotine (optional): found in different strengths, or not at all in zero-nic vapes.
According to Public Health England, regulated e-liquids do not contain tar or carbon monoxide — the most harmful components of cigarette smoke.
Why it feels like smoking
Many vape liquids use PG to give that familiar throat hit — the slight scratchiness that mimics smoking. VG, on the other hand, produces thicker clouds. The balance between PG and VG influences both flavour intensity and vapor production.
What about safety?
- Temperature control: modern devices avoid overheating and dry hits.
- Coil lifespan: changing coils regularly prevents burnt taste and build-up.
- Battery quality: stick with certified brands to avoid short circuits.
When used properly with regulated e-liquids, vaping is widely accepted by UK health agencies as significantly less harmful than smoking — though not risk-free.
Final puff: understanding is power
Knowing what goes into your device — and your lungs — is step one to vaping smarter. Whether you’re new to vaping or just curious, understanding the process demystifies the habit and helps you make more informed choices.
Explore trusted vape kits
Want to try it yourself or upgrade your setup? Browse our starter vape kits and UK-tested e-liquids to find a smooth, satisfying experience backed by science.
